Energy Carrier Defined
An energy carrier is a substance or a phenomenon containing energy convertible to useful mechanical or electrical energy. The most common type of energy carrier is fuel, such as gasoline, natural gas, or coal.
Electricity is also a form of energy that can be carried through wires and used to power machines and appliances.
Green Hydrogen as an Energy Carrier
What Is Hydrogen?
Hydrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless gas. It comprises one proton and one electron, and it is the lightest, most abundant element in the universe. It constitutes approximately three-quarters of the universe's elemental mass.
Three Main Types of Hydrogen
Hydrogen can be classified as either gray, blue, or green hydrogen depending on the source of energy and the production method applied in making the molecular hydrogen.
Gray Hydrogen
The main energy source for gray hydrogen is fossil fuels, such as natural gas or coal. It is the most common type of hydrogen produced today.
The production methods for gray hydrogen involve steam methane reforming and coal gasification, which release carbon dioxide.
Hence, gray hydrogen has a carbon footprint.
Blue Hydrogen
Blue hydrogen is a type of hydrogen produced from natural gas using steam methane reforming and coal gasification. It has close similarities to gray hydrogen except for the fact that most of its carbon emissions are sequestered.
This process of sequestration is called carbon capture and storage (CCS). Carbon dioxide is captured before its subsequent emission into the atmosphere, compression, and transportation to an appropriate storage site.
Hence, blue hydrogen will count as a low-carbon fuel. It is a cleaner alternative than gray hydrogen but costs more because of CCS.
Green Hydrogen
Green hydrogen is made from clean, renewable sources, such as solar, wind, or water power.
This type of hydrogen is produced through electrolysis, which splits water into hydrogen and oxygen using an electric current. This process leaves nothing but oxygen as a by-product.
While an expensive process, the production of green hydrogen is more environmentally-friendly than other hydrogen production methods as it does not generate emissions.
Why Is Green Hydrogen an Ideal Energy Carrier?
Hydrogen has emerged as a potential replacement for traditional fuels as an energy carrier.
For 2022, the U.S. Department of Energy has invested more than $330 million into the research and development of hydrogen and fuel cells.
Several countries have also looked into investing in green hydrogen to help achieve their clean energy goals.
Green hydrogen is non-toxic and does not release any harmful emissions when burned.
According to an analysis by the Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy, hydrogen and fuel cells have the following potential to reduce emissions:
- Light-duty highway vehicles enable an emission reduction of 50% to over 90% over today's gasoline vehicles
- Specialty vehicles have more than 35% reduction versus current diesel and battery-operated lift trucks
- Transit buses show fuel savings roughly 1.5 times greater than diesel internal combustion engine buses
Main Applications of Green Hydrogen as an Energy Carrier
Hydrogen can generate energy in a variety of ways. The following represent some of the most common applications:
Transportation
Hydrogen can power cars, buses, and other vehicles. In this application, it is known as a hydrogen fuel cell. A fuel cell combines hydrogen and oxygen to create electricity. The only emissions from the vehicle are water vapor.
Heating
Residential and commercial buildings constitute one of the most sizable users of energy. Relying mainly on fossil fuels for the daily use of certain products, this sector accounts for 13% of the 2020 greenhouse gas emissions in the United States.
Hydrogen can provide heating for these buildings, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels.
Petroleum Refining
Hydrogen can process oil and natural gas. It removes sulfur and other impurities from these substances.
Industrial Processes
Hydrogen is also used in numerous industrial processes, including metal production, fertilizer manufacturing, and refining.
Chemicals
Hydrogen is used in the manufacture of chemical products, including ammonia, methanol, and plastics.
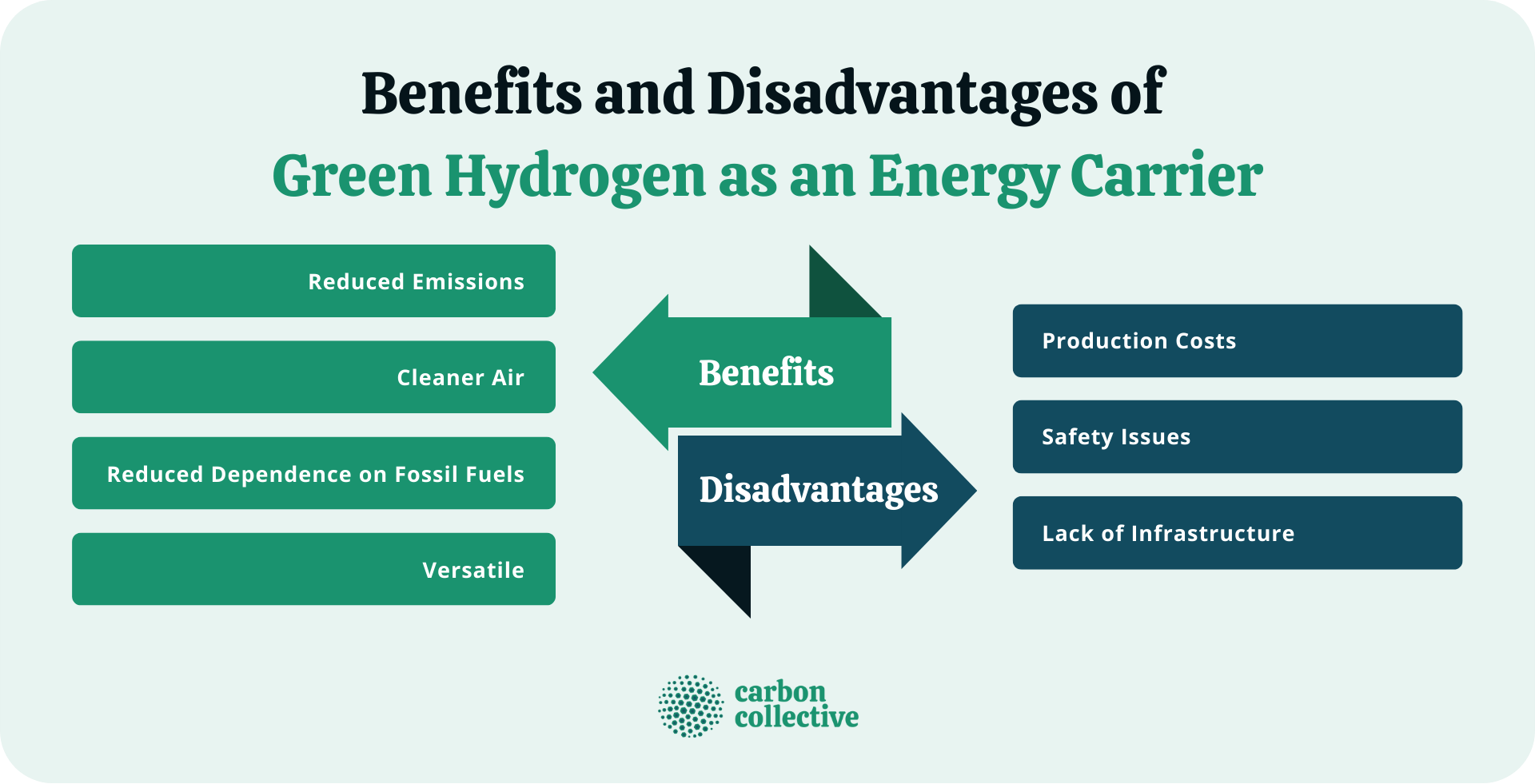
Benefits of Green Hydrogen as an Energy Carrier
The benefits of green hydrogen as an energy carrier include the following:
Reduced Emissions
Green hydrogen contributes to reduced emissions since it does not produce any harmful pollutants when burned.
In addition to helping reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change, it contributes to improved air quality and public health.
Cleaner Air
Burning green hydrogen releases only water vapor and heat. There are no harmful emissions, such as carbon dioxide or nitrogen oxides. This makes it a cleaner alternative to traditional fuels.
With cleaner air, people can reduce their exposure to respiratory problems.
Reduced Dependence on Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels are a major contributor to global warming. Using green hydrogen can help reduce our dependence on fossil fuels, which is not sustainable in the long run.
Hydrogen can also help us make more efficient use of our resources.
Versatile
Green hydrogen is a versatile fuel with a variety of applications, such as transportation, heating, and industrial processes.
This makes it an attractive option for countries looking to switch to clean energy.
Disadvantages of Green Hydrogen as an Energy Carrier
Along with the benefits, green hydrogen has its disadvantages:
Production Costs
Producing green hydrogen through the process of electrolysis is not cheap. It requires investment in new technology and infrastructure.
Safety Issues
Due to its flammable nature, hydrogen can be dangerous if not handled properly. Extensive safety measures must be in place to ensure its safe usage.
Lack of Infrastructure
Currently, there is a lack of infrastructure for green hydrogen. This can create difficulties finding or using it and will require evaluation if hydrogen is to become a viable energy source.
This will need to be addressed if hydrogen is going to become a major source of energy.
Other Energy Carrier Examples
Several other energy carriers can generate electricity. Some of these include:
Biofuels
Biofuels are fuels derived from biomass or organic matter. The most common type of biofuel is ethanol, made from sugarcane or corn.
Biofuels can be used in vehicles, generators, and other devices.
Although they can reduce carbon footprint, biofuels are not the solution to our energy needs. These fuels can still have a potentially undesirable environmental impact.
Methanol
Methanol is a fuel made from natural gas or coal. It can be used in vehicles and other devices to generate electricity.
Methanol is less polluting than other fossil fuels. It is also relatively cheap to produce and has a high energy density.
However, this type of fuel emits harmful pollutants when burned.
The Bottom Line
Energy carrier is a term used to describe any substance containing energy that can power machines or devices. There are various energy carriers, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Green hydrogen is an environmentally-friendly option with several benefits over other energy carriers. Green hydrogen has a variety of applications, is easy to transport, and does not produce harmful emissions.
However, it is not cheap to produce and requires a developed infrastructure. Due to its flammable property, extensive safety measures must be in place to ensure its safe usage.
Other energy carriers include biofuels, methanol, and fossil fuels. Each has its benefits and drawbacks.
Which energy carrier is best for the future depends on different factors, including cost, availability, and emissions.
FAQs
1. What is an energy carrier?
An energy carrier is any substance that contains energy used to power machines or devices. This includes things like gasoline, diesel fuel, natural gas, and coal.
2. What is green hydrogen?
Green hydrogen is a type of hydrogen produced through electrolysis. This means that it is made from water using renewable sources, such as solar or wind power.
3. What is electrolysis?
Electrolysis is the process of separating bonded elements by passing an electric current through them. In the case of green hydrogen, this means separating water into hydrogen and oxygen gas.
4. What does CCS mean?
CCS stands for carbon capture and storage. This process captures CO2 from different sources, such as factories and power plants, and stores it underground in a secure location to prevent it from entering the atmosphere.
5. What are fuel cells?
Fuel cells convert energy from fuel into electricity. These cells can run on a variety of fuels, including hydrogen, ethanol, and methanol.