What Is a Free Market Economy?
A free market economy is an economic system in which the production and distribution of goods and services are determined by the free market rather than by central planning.
In a free market economy, businesses and individuals operate in a largely unregulated market, with little government interference. Supply and demand, rather than government regulation, determine prices.
There are several benefits to a free market economy. One of the main advantages is that it allows for economic freedom and choice.
Individuals can choose what they want to produce, how they want to produce it, and what they want to consume. This type of economy also provides an incentive for businesses to utilize efficient, innovative production processes.
What Is a Free Market?
A free market is a market system in which the prices for goods and services are determined by the open market and not by any central authority.
In a free market, the laws and rules that govern an economy are set by market forces rather than by some central government or regulatory agency.
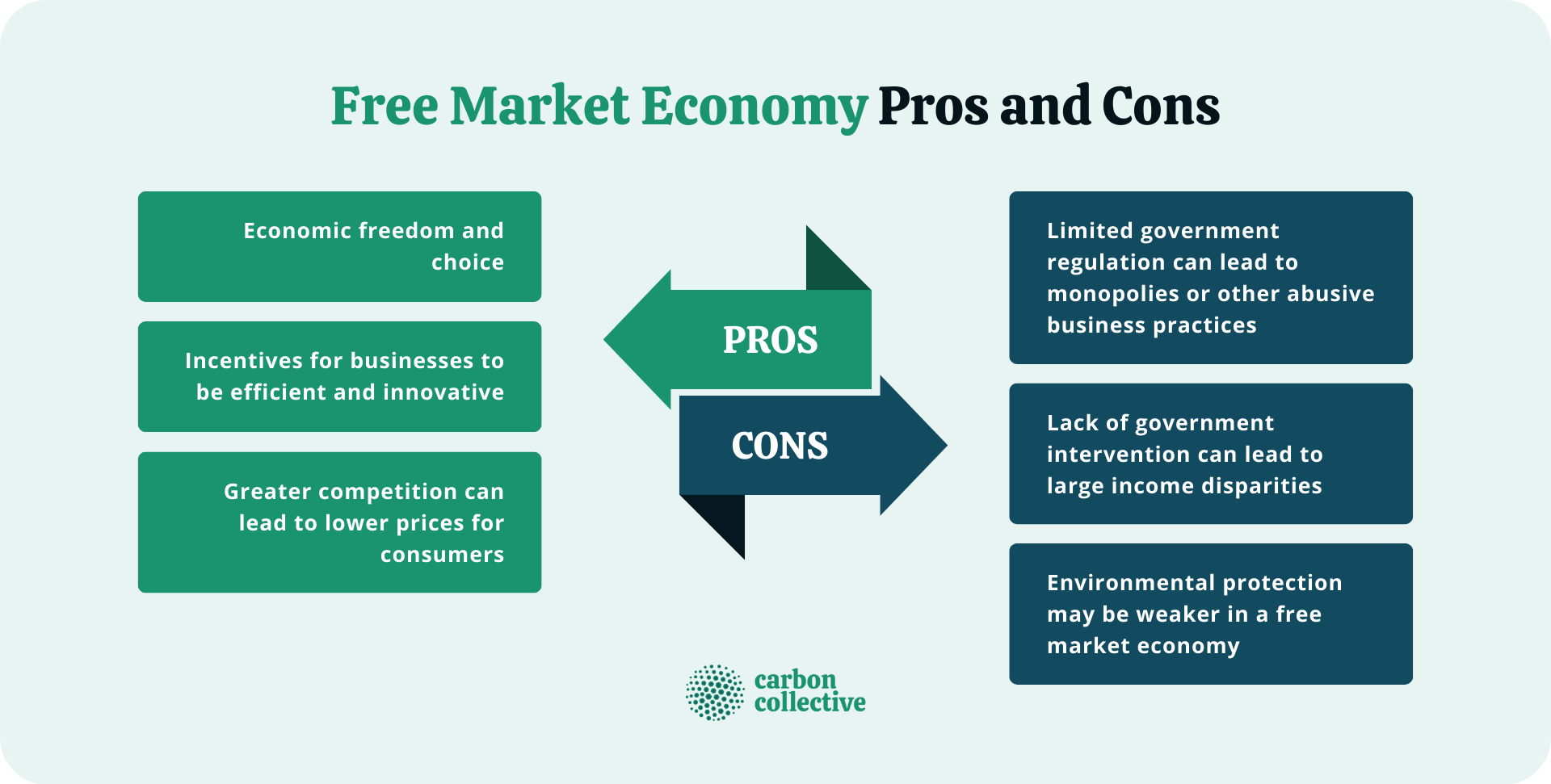
Free Market Economy Pros and Cons
Here are some pros and cons of a free market economy:
Pros
- Economic freedom and choice
- Incentives for businesses to be efficient and innovative
- Greater competition can lead to lower prices for consumers
Cons
- Limited government regulation can lead to monopolies or other abusive business practices
- Lack of government intervention can lead to large income disparities
- Environmental protection may be weaker in a free market economy
Command Economies
A command economy is an economic system in which the government controls what is produced and how it is sold.
In a command economy, the government decides what and how much to produce and what price to charge for goods and services.
The Free Market as an Information Source
One of the main advantages of a free market economy is that it provides a way for businesses and consumers to exchange information about what they want and need.
In a free market, businesses can offer new products and services in response to consumer demand, and consumers can choose which products and services they want to buy.
Free Markets and Regulation
Although a free market is typically unregulated, some cases require government regulation.
For example, the government may need to regulate businesses to protect consumers from fraud or dangerous products. The government may also need to provide infrastructures, such as roads and bridges, that businesses cannot.
A free market economy is an economic system that allows for economic freedom and choice. It provides a way for businesses and consumers to exchange information and may face regulation by the government.
The Bottom Line
A free market economy is an economic system that allows for economic freedom and choice. It provides a way for businesses and consumers to exchange information and may face regulation by the government.
The free market economy has pros and cons, but it remains a popular economic system.
FAQs
1. Is a free market economy the same as capitalism?
No. The terms "free market economy" and "capitalism" are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same. A free market economy is a type of economic system, while capitalism is an economic and political system. Capitalism is based on private ownership of the means of production and involves an open market with little to no government intervention. Free market economies, on the other hand, can be based on public or private ownership of the means of production, and they may have varying degrees of government intervention.
2. What if there is no competition in the free market?
If there is no competition in the free market, it is not a truly free market. A free market requires that businesses compete for consumers' business. If there is only one business in a particular industry, that business has a monopoly and does not operate in a free market. Monopolies are not allowed in a free market economy.
3. How healthy is competition in a free market economy?
Competition is healthy in a free market economy because it keeps businesses innovative and efficient. If there is no competition, businesses have no incentive to improve their products or services or lower their prices. In a free market, businesses that do not compete effectively will eventually go out of business. This ensures that only the strongest and most efficient businesses survive.
4. Is the free market subject to business cycles?
Yes. Free market economies are subject to business cycles, just like any other economy. Business cycles are periods when the economy grows and expands, followed by periods when the economy contracts and shrinks. In a free market economy, businesses expand and contract in response to changes in consumer demand. When consumer demand is high, businesses will expand, and when it is low, they will contract. This can lead to periods of economic growth followed by periods of recession.
5. What happens if there are illegal activities in the free market?
If there are illegal activities in the free market, then those businesses will be subject to punishment by the government. The government may fine them, shut them down, or prosecute them. The government does not intervene with the free market but steps in when illegal activities occur. This helps ensure that the free market remains fair and safe for everyone involved. Illegal activities in the free market can include things like fraud, price-fixing, and anti-competitive practices. These activities can harm consumers, businesses, and the economy as a whole.