A general ledger, also known as an accounting ledger, is the master record that provides summaries for all transactions in the various accounts used by a company.
You can think of each of the company accounts as a notebook filled with transactions for that account. So, for example, the cash account is a notebook that records all of the transactions the business makes using cash.
Expanding on this, the general ledger is like a folder that contains all of the notebooks for each account. The ledger is a summary or record of all of these individual account records.
The general ledger is also known as the book of second entry or the book of final entry. This is because all events are first recorded in journals before being posted to the ledger at the end of the accounting cycle period.
Types of General Ledgers Accounts
General ledger accounts are categorized into 5 main accounts. These accounts are used separately for a better understanding and higher accuracy for accountants when recording entries.
Asset Account
In a general ledger, the asset account records all the assets which are owned by a proprietorship. There are two types of assets. Current assets and non-current assets. The non-current assets have a life of more than 1 year, however, they are not easily converted into liquid form as compared to current assets, which are those assets who have a period of less than 1 year.
Examples of non-current assets are vehicles, land and buildings. On the other hand, inventory, cash and account receivable are the examples of current assets. In a general ledger, the opening balance of assets is recorded on the debit side. As the value of an asset increases, the debit side increases, conversely as the asset value decreases, the credit side increases.
Liability Account
This account shows the money a business owes to another company, after a certain period. Like assets, there are two types of liabilities recorded in the general ledger. Short-term liabilities, which have to be paid back within 1 year, while the long-term liabilities have to be paid back are due after one year.
Examples of long-term liabilities are long term loans and mortgage, while the short-term liabilities are considered as account payables, interest payables and short-term loans. In the general ledger, the opening balance of a liability account is posted on the credit side. The higher the debt, the balance on the credit side will increase, although a decrease in debt will reduce the credit side, by increasing the debit side column.
Revenue Account
The general ledger revenue account records the income earned by a business from its buyers after the sale of certain goods and services. The revenue accounts opening balance is filed on the credit side column. Examples of revenue accounts are sales revenue account and fee earned for performing services. The greater the revenue, the credit side increases.
Expense Account
The expense account records the outflow of money from the business for the payment of salaries, advertising and delivery. The expense account is recorded on the debit side of the general ledger.
Equity Account
The equity account in a general ledger is recorded on the credit side. This account shows us the total capital invested by the owners into the business, in addition to the profits and losses earned and further investment of shareholders into the company. The equity account differs from business to business, depending on the size and the structure. For example, a public limited company’s account will have an account of shareholders investment.
General Ledger and Double Entry
Everyone needs to know the relationship between the double-entry system and the general ledger to understand the rules of debit and credit and how the balances are recorded in each account, as explained above in the ledger accounts section.
The double entry system states, that there should be 2 entries for one transaction in their specific accounts, this is the reason why the general ledger records two sides of each financial transaction, one on the debit column and the other on the credit side column.
For instance, Company A sells its goods to Company B for cash. This transaction will have 2 corresponding entries. Cash will be debited as cash is an asset and assets are recorded on the debit side of the account, while sales revenue will be recorded on the credit side.
How to Use A General Ledger
T-Account
A general ledger is made through the use of a T-account—which is a graphical representation of a general ledger account. This account is known as the “T” account because it takes the shape of the letter “T” when constructing an account.
The debit side is recorded on the left side of the account, while the credit side is recorded on the right-side column. Here’s how a T account is made:
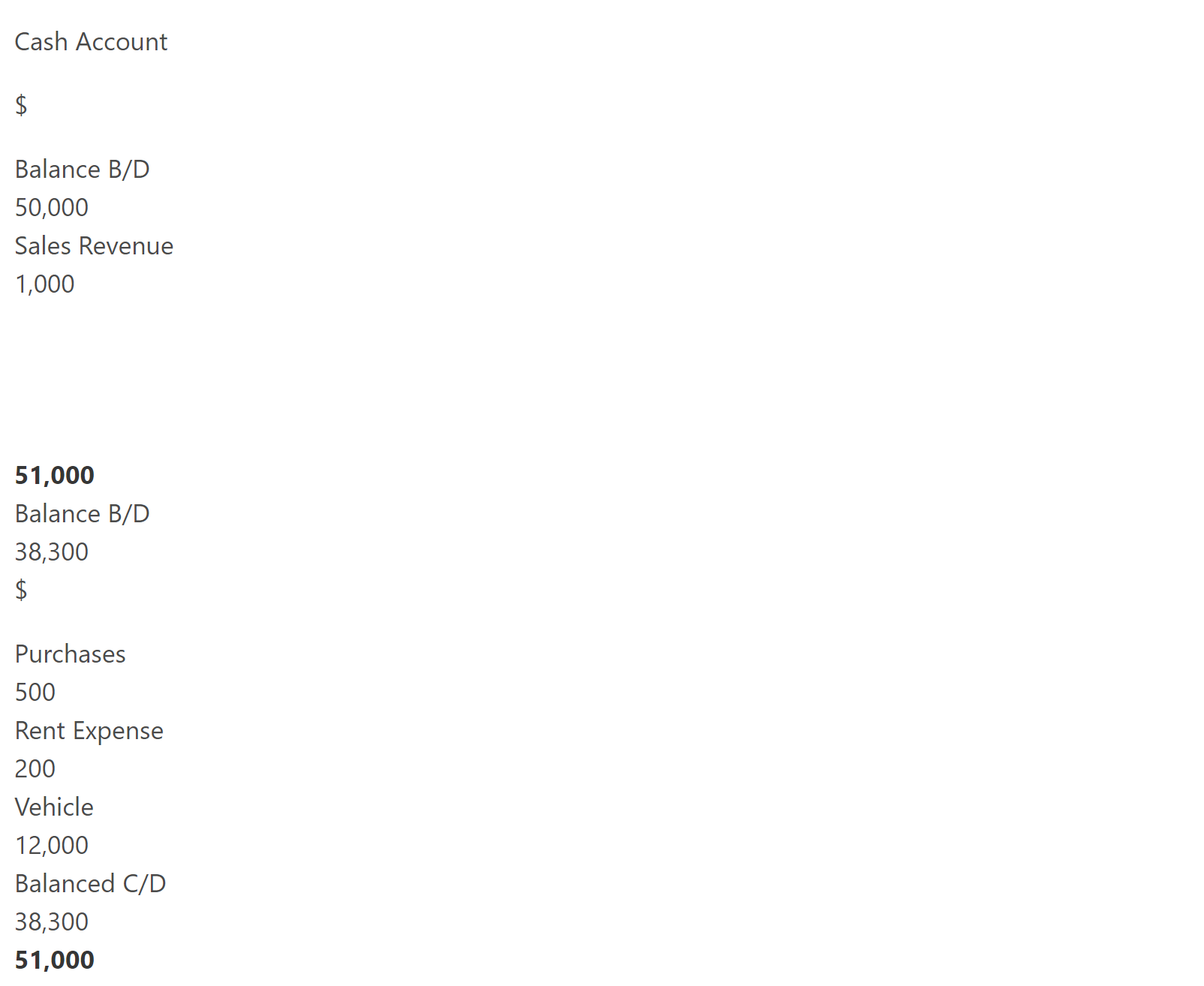
This is an example of at account which shows us a cash account, which has an opening balance of 50,000 filed on the debit side. All costs which reduce cash balance, are recorded on the credit side like purchases and vehicle bought for cash. After all the cash expenses and cost are posted in the cash account, the new balance for the next accounting period is $38,300.
The Ledger Account
After all the T- accounts are made, all of these accounts will be recorded into the general ledger in a collective order, which shows the set of financial accounts of the company. For example, all accounts related to assets will be recorded into the asset account.
All accounts in a general ledger are listed with their transactional data and account numbers. Let us look at how a general ledger is made in a debit and credit composition.
General Ledger
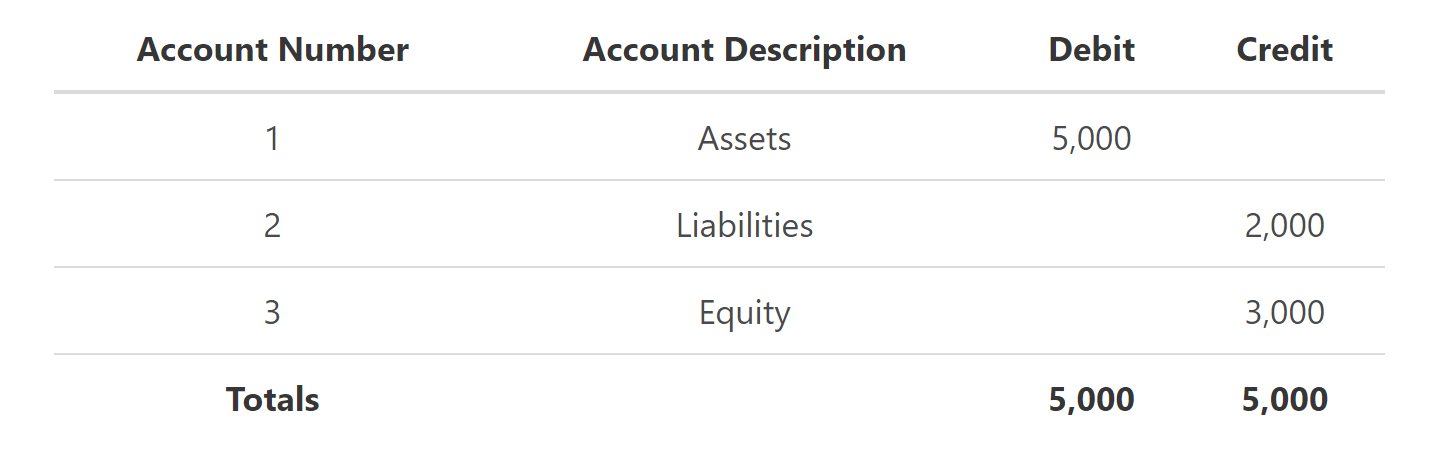
The general ledger shows us the balances between all the accounts, along with the account titles and numbers. It is also important to make sure when making a general ledger, that assets, liabilities and equity should equal each other according to the accounting equation as shown in the example of the ledger account constructed above.
Uses of General Ledger
The general ledger accounting format is one of the most important tools for any company. It is mainly used to improve the accuracy of managing accounts and having the ease to access any account at any time. It is also used to monitor the financial position of any business, through the help of financial statements such as the balance sheet and the income statements.
FAQs
1. What is a general ledger?
A General Ledger (GL) is a financial statement that shows the various assets, liabilities, and equity of a company at a given point in time. The GL can be used to track overall performance, assess financial position, and make business decisions.
2. What does a general ledger tell you?
A general ledger tells you about the balances between all the accounts of a company, as well as the account titles and numbers. It is used to improve accuracy when managing accounts, as well as to monitor the financial position of a business.
3. What is the purpose of a general ledger?
The purpose of a general ledger is to improve accuracy when managing accounts, as well as to monitor the financial position of a business. It does this by providing a collective view of all the company's accounts and their respective balances.
4. What are the types of general ledger accounts?
The types of general ledger accounts are assets, liabilities, and equity. They are all listed in a debit and credit composition, in order to show the balances between them.
5. is the difference between general journal and general ledger?
The general journal is a temporary account, which is used to record all the transactions of a company. The general ledger is a permanent account, which is used to show the balances between all the accounts of a company.
