What Is Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG)?
LPG is a fossil fuel used as a source of energy which means it is not renewable.
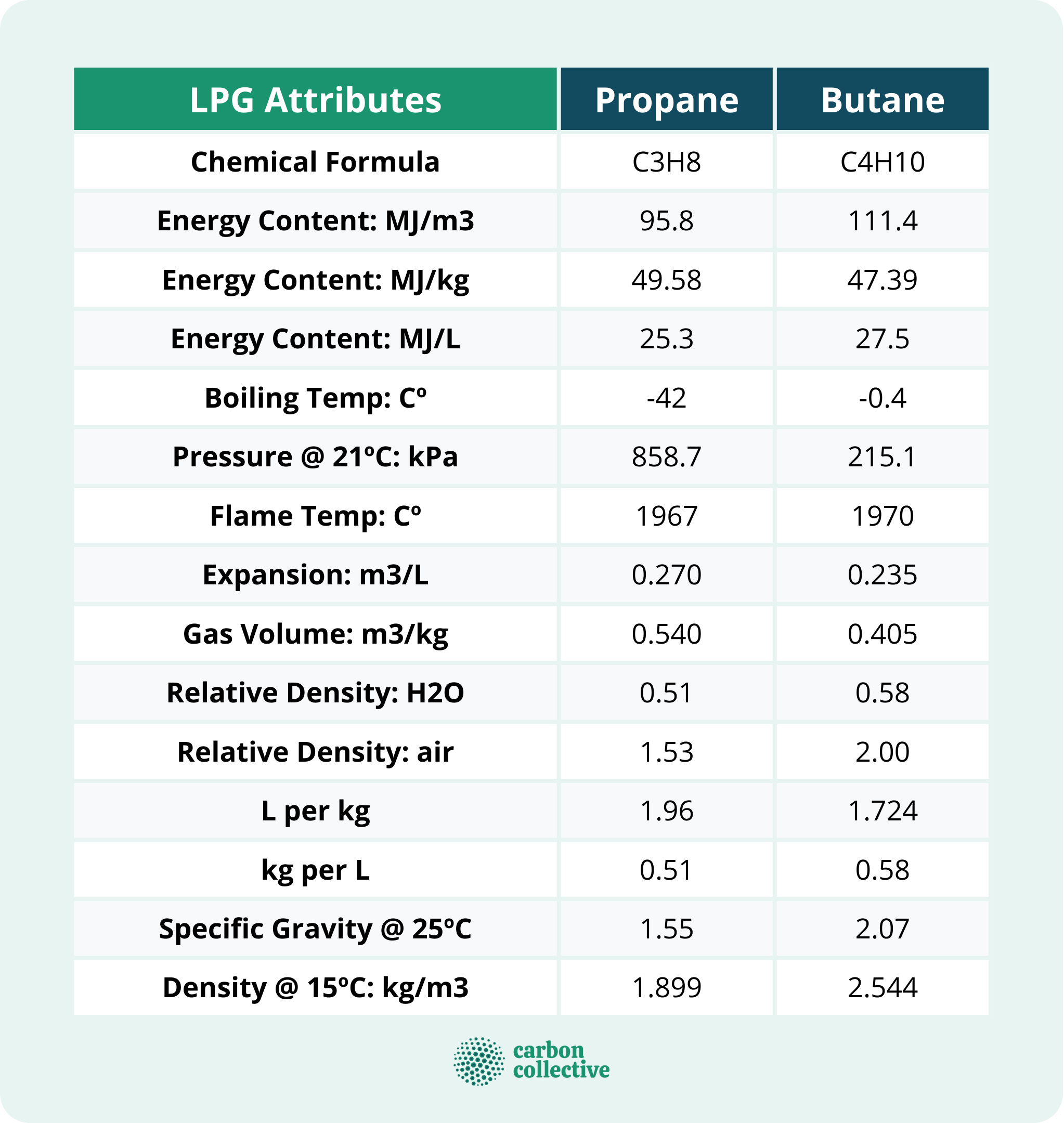
It is a flammable hydrocarbon gas mixture composed of hydrocarbons with three or four carbon atoms. Thus, the typical LPG components are propane (C3H8) and butane (C4H10). Other hydrocarbons may be found in trace amounts.
LPG burns well in the air and has a similar energy content to gasoline and twice the heat energy of natural gas. As a result, it is a wonderful fuel for heating, cooking, and automobiles.
Usually, a steel container or cylinder holds the gas under pressure, or a tank keeps it in liquid form. The pressure within the container is determined by the kind of LPG (commercial butane or commercial propane) and the temperature outdoors.
LPG vs. Natural Gas
LPG has a higher energy content than natural gas, so it takes less gas to create the same quantity of heat. The second important distinction is the oxygen-to-gas ratio necessary for optimal combustion. LPG requires an oxygen-to-gas ratio of about 25 to 1 and a 10 to 1 ratio for natural gas.
Here are more detailed differences between LPG and Natural Gas:
- LPG is composed of propane and butane, whereas natural gas is composed of methane.
- Different formulae: In LPG, Propane is C3H8, Butane is C4H10, and Methane is CH4 in natural gas.
- LPG is heavier than air, while natural gas is lighter than air.
- LPG has a larger energy content of 93.2MJ/m3 than natural gas, which has a value of 38.7MJ/m3.
- LPG requires a greater air-to-gas ratio for burning, at 25 to 1, compared to 10 to 1 for natural gas.
- Unlike natural gas, which is cryogenically converted to liquefied natural gas (LNG), LPG is liquefied by pressurization.
- LPG is delivered in gas bottles and tanks, whereas natural gas is delivered by pipeline.
- LPG appliances use 2.75 kPa as opposed to 1.1 kPa natural gas appliances.
Components of LPG
LPG consists of two major components: propane and butane.
Propane
Propane is the main component of LPG, making up approximately 60-70% of the gas. It is also the most popular LPG fuel because it has a high energy content and burns cleanly with no soot or ash.
Because of its lower boiling point is ideal for outdoor storage and is largely utilized for central heating, commercial uses, cooking, and transportation.
Propane is also non-toxic and does not contaminate water or soil.
Butane
Butane is the second major component of LPG, making up approximately 30-40% of the gas. It is a less popular fuel than propane because it has a lower energy content and can be more difficult to ignite.
It is often transported in cylinders for portable applications such as portable heaters or recreational vehicles such as boats, caravans, and grills.
Butane may also be used as a propellant, a refrigerant, and as a fuel for welding torches.
Manufacturing LPG
LPG is a by-product of natural gas extraction and crude oil refining.
Natural gas is a mixture of methane and other gasses, including propane and butane. When natural gas is extracted from the ground, the propane and butane are separated from the methane.
These other gasses are then liquefied and stored under pressure until they are ready to be used.
LPG can also be made from crude oil, which is refined into gasoline and other petroleum products. The propane and butane are separated from the other products and liquefied for storage.
Storing LPG
LPG is compressed into a liquid at low pressures and stored in specially engineered gas bottles, cylinders, or tanks. The temperature determines the pressure - the warmer it is, the higher the pressure.
It is usually stored as a liquid in steel or composite containers ranging in size from tiny BBQ gas bottles to big gas cylinders and LPG storage tanks.
LPG is a very stable gas that will not explode if properly stored. However, if there is a leak in the storage tank, the LPG can escape and build up in the atmosphere. If there is enough LPG and the right conditions, the gas can ignite and cause an explosion.
Uses of LPG
LPG is a versatile fuel that can be used for a wide range of applications, including the following:
At Home
- For cooking
- For heating
- For hot water
- For drying clothes
For Businesses
- As a fuel for forklifts and other commercial vehicles
- As a heat source for industrial processes
- As a refrigerant
For Leisure
- Camping
- Boating
Benefits of LPG
LPG has several benefits over other fossil fuels. Here are some of the most notable:

- It is cleaner burning than other fossil fuels. This means that it produces emissions when burned, but these emissions are lower.
- It is more efficient than other fossil fuels. This means that it produces more energy per unit of fuel.
- It is less expensive than other fossil fuels. This means that it costs less to use LPG than other fossil fuels, which makes it a more affordable option for consumers.
- It is a portable fuel source. This means that it can be easily transported and stored, making it a convenient option for many consumers.
Safety Tips and Precautions
LPG cylinders, tanks, and bottles are typically safe to use when utilized properly. The following are some safety guidelines to help you take the appropriate measures when using LPG.
Maximum Pressure Rating
The maximum pressure level of the propane tank is the propane tank's design LPG pressure limit.
While propane tanks are designed to handle far greater pressures than usual running LPG pressures, it is nevertheless vital not to exceed the maximum pressure rating of the propane tank.
Exceeding the maximum pressure level of an LPG tank can cause a propane tank explosion.
Leak Checks
Regularly checking your LPG system for leaks is crucial, especially if you have not used your system in a while.
Mix a solution of equal parts water and dish soap to check for leaks. Apply the solution to all LPG connections and fittings. If the solution bubbles, you have a gas leak.
If you detect a gas leak, immediately turn off the LPG tank valve and do not attempt to repair the leak yourself. Call a qualified technician to repair the leak.
Safe Storage
Always store your LPG cylinders upright when not in use and secure them to prevent them from falling over.
Do not store LPG cylinders in direct sunlight or in an enclosed space, such as a car trunk, where they could overheat.
Conclusion
LPG is a pressurized liquid gas extracted from natural gas and crude oil refining. It is a versatile fuel that can be used for a wide range of applications, including cooking, heating, hot water, drying clothes, forklifts, and other commercial vehicles.
When using LPG, it is important to follow safety guidelines to prevent accidents. Store LPG cylinders properly and keep them secure to prevent them from falling over.
Please consult a qualified professional if you have any questions about using LPG.
FAQs
1. What is Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG)?
LPG is a pressurized liquid gas that is extracted from natural gas and crude oil refining. It is composed of propane and butane.
2. What is the difference between LPG and Natural Gas?
LPG has a higher energy content than natural gas, so it takes less gas to create the same quantity of heat. The second important distinction is the oxygen-to-gas ratio necessary for optimal combustion. LPG requires an oxygen-to-gas ratio of about 25 to 1, while natural gas requires a 10 to 1 ratio.
3. What are the components of LPG?
LPG is composed of propane and butane.
4. What is propane?
Propane is a flammable hydrocarbon gas that is liquefied by pressurization and is derived from natural gas processing and oil refining. It is most typically used for heating and cooking, although it has a broad range of domestic and commercial applications, from home water heaters to a restaurant's kitchen.
5. What is butane?
Butane is a combustible hydrocarbon gas produced by natural gas processing and oil refining. However, butane is more widely employed as a fuel, propellant, and refrigerant.