A power inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) to standard alternating current (AC).
Electricity is sustained at a constant voltage in one direction in AC. On the other hand, in AC, electricity flows in both directions in the circuit as the voltage changes from positive to negative.
With a power inverter, you can plug in your appliances and devices. You can power them as you would through an electrical outlet in a house.
An inverter enables you to utilize the electricity generated by a car, truck, or boat batteries or a renewable energy source like wind turbines or solar panels to power electronics, home appliances, and other electrical equipment.
How Do Power Inverters Work?
Fundamentally, the inverter turns a DC input into an AC signal by switching the direction of the current very rapidly. As a consequence, a DC input becomes an AC output.
For instance, when a cell phone is plugged into the car cigarette lighter, it supplies DC power. This must be converted to AC with an inverter for your device's battery to charge smoothly.
Filters and other electronics can be utilized to create a voltage that varies as a clean, repeating sine wave that can be fed into the power grid.
This sine wave is a shape or pattern the voltage creates over time. It is the pattern of power that the grid can utilize to ensure that there are no electrical equipment damages.
A sine wave is built to operate at specific frequencies and voltages.
A power inverter is a device that uses electrical circuits to change the direction of DC power flow, making it alternate like AC power.
These oscillations are harsh and produce a square waveform rather than a rounded one. Filters are needed to smooth out the wave so that more electrical devices may utilize it.
Since most electronic devices are intended to be connected to a conventional wall socket, which provides AC power, they need AC power to function correctly.
Two Types of Power Inverters
Most current power inverters generate either modified square waves or pure sine waves.
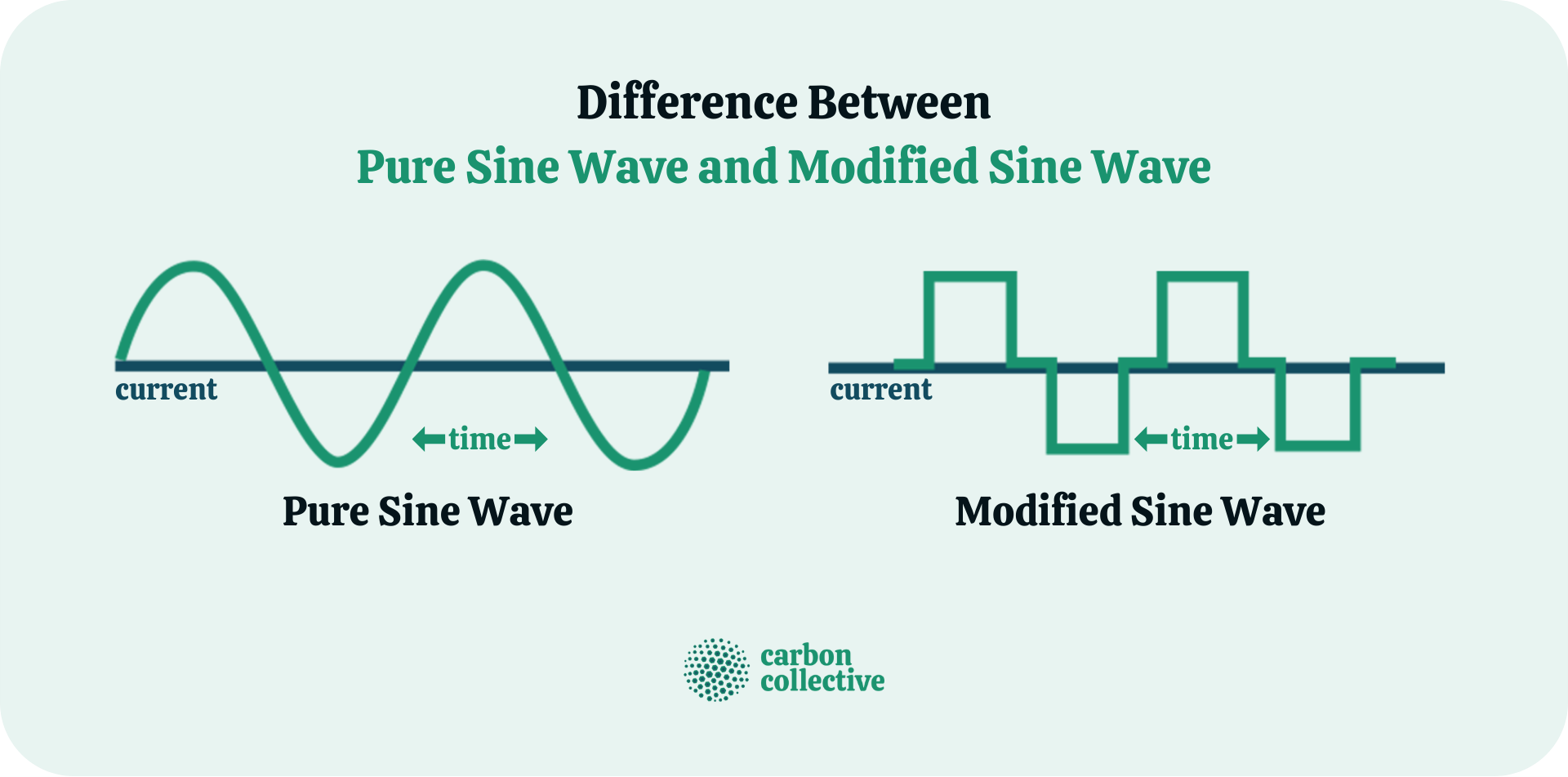
Prices for Pure Sine Wave inverters are higher, but they are also more powerful and efficient. This type of inverter produces a sine wave with the same quality of power provided by the main power utilities.
Pure Sine Wave is beneficial for powering high-energy-consumption electrical devices and equipment.
The devices that need pure sine wave inverters include:
- Audio and video equipment, satellite systems
- Other devices, like bread makers, certain battery chargers, and light dimmers
- Appliances with AC motors, such as refrigerators, compressors, or microwaves
- Certain medical equipment, such as many CPAP devices for sleep apnea and oxygen concentrators
Modified Sine Wave
Modified Sine Wave inverters are substantially less expensive than Pure Sine Wave inverters and can only power a limited number of household appliances and fixtures.
However, high-energy-consuming equipment and devices, such as computers, microwave ovens, air conditioners, and heaters, may not be powered by this type of inverter.
Generally, motors in modified square wave inverters will run hotter and likely will not last as long because the total harmonic distortion is higher.
Modified square wave inverters will also cause a "buzz" that can be heard from audio devices and some other appliances such as ceiling fans and microwave ovens.
Different Uses of Power Inverters
Inverters are used in a wide range of applications.
DC Power Source Usage
An inverter converts direct current (DC) power generated by batteries or fuel cells to alternating current (AC).
The electricity can be at any voltage necessary. For instance, power AC equipment built for mains operation or rectified to create DC at any desired voltage.
Other power inverters include jumper-like wires that can be connected directly to a battery. This is necessary to supply more powerful equipment.
Uninterruptible Power Supplies
When mains power is unavailable, an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) utilizes batteries and an inverter to provide AC power.
A rectifier produces DC electricity to replenish the batteries when the main power is restored.
The Federal Energy Management Program (FEMP) presented acquisition guidance for uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). UPS is a product category under the ENERGY STAR efficiency requirements.
Federal laws and requirements mandate that agencies acquire ENERGY STAR-qualified products or FEMP-designated products in all product categories under these programs and in any acquisition actions that are not specifically exempted by law.
In Refrigeration Compressors
To adjust system performance, an inverter can be used to manage the speed of the compressor motor to drive variable refrigerant flow in a refrigeration or air conditioning system.
In Entertainment Devices
Power inverters can be used in entertainment devices such as televisions and DVD players to convert DC power from batteries into the AC needed to produce a picture.
Industrial Power Supplies
An inverter can also provide electrical power for industrial applications such as robotics, solar photovoltaics (PV), and standard and customized power tools.
Carriers, Sources & Other Devices
Inverters can be used with batteries as a direct DC-to-DC converter to provide a charging current on the input side or supply power on the output side.
In some cases, an unregulated or fixed voltage source is connected to an inverter's input terminals used to produce a regulated or adjustable voltage at the inverter's output terminals.
Inverters are used for AC motor speed control in film projectors, peristaltic pumps in intravenous infusion, syringe pumps in liquid dispensing, and are also being explored for high-powered lasers.
Power inverters are also used in renewable energy applications to provide AC power from battery sources.
Capacity of Inverters
The capacity of an inverter refers to the amount of power that the unit can continuously supply.
The inverter's rating must be at least 25% more than the total power needed by all connected appliances when they operate concurrently.
Multiple inverters can be connected in series or parallel to get the desired capacity.
Models of power inverters would vary in how many watts they can generate.
An inverter's capacity should equal the entire number of watts required by each device, plus at least 50% more to accommodate for power use peaks or spikes.
An inverter needs to supply two needs: Peak or surge power and Typical or usual power.
Peak or Surge Power
Surge is the highest power that the inverter can provide, often for a brief period of time in a few seconds to around 15 minutes time range.
Certain appliances, particularly those powered by electric motors, require a far bigger beginning surge than they do while running. Pumps are the most common example; refrigerators are another.
Typical or Usual Power
Typical is the amount of power that the inverter must generate on a continuous basis. This is referred to as continuous rating. This is typically far less than the surge.
For instance, this is the current drawn by a refrigerator once the motor starts up, the current drawn by a microwave - or the current drawn by all loads combined.
Average power is generally much less than typical or surge power and is rarely a factor in selecting an inverter.
If you operate a pump for 20 minutes and a tiny TV for 20 minutes over the course of an hour, the average may be just 300 watts, despite the pump's 2000 watts needed.
Average power is solely relevant for determining the required battery capacity. Inverters must be sized for both peak and continuous loads.
Key Takeaways
- Inverters convert DC power from an energy source, such as a battery or solar panels, to AC power for use in any household appliance.
- Inverters vary in capacity and wattage. Inverters with larger power output can be connected in parallel or series to produce more wattage.
- Inverters that supply a pure sine wave operate at a higher price range than inverters that provide a modified sine wave.
- Peak or surge power is the highest amount of power the inverter can provide, while typical or usual power is the amount of power that the inverter will provide.
FAQs
1. What is a power inverter?
A power inverter is a device that changes DC current to AC current. It increases the voltage, allowing electricity to be transported through long distances, then decreases the voltage once it reaches its destination in order to use it
2. Can I connect more than one inverter to a power source?
Yes, you can connect multiple inverters in parallel or series to increase your capacity. You may also want to consider using batteries as an energy buffer between your devices and the power sources.
3. Can I use a car battery as an energy buffer?
You can, but there are some risks. The average life span of your car battery is usually around two years. There should be no problem if you're using it for less than that time frame. You'll need to recharge your batteries regularly or purchase new ones if they fail before the end of their average life span.
4. Where can I get a power inverter?
There are many places that offer power inverters, such as electronic stores, home improvement stores, and online. Remember to ensure that the inverter is right for your needs before purchasing it.
5. How are different power inverters priced?
Power inverters vary in price depending on the watts they can generate. The higher the wattage, the more expensive it is. You may also need to consider whether you want a pure sine wave inverter or a modified sine wave inverter.
