What Is a Pension Plan?
A pension plan is a retirement savings plan sponsored by an employer. It is a type of defined-benefit plan, which means that it pays a predetermined monthly benefit to retirees based on their years of service and salary history.
These payments are guaranteed to be paid for the retiree's lifetime and may also include a survivor benefit for a spouse or other beneficiary.
Pension plans are funded by employer contributions and investment earnings. Employees do not typically contribute to pension plans.
Advantages of a Pension Plan
Below are some advantages of a pension plan:
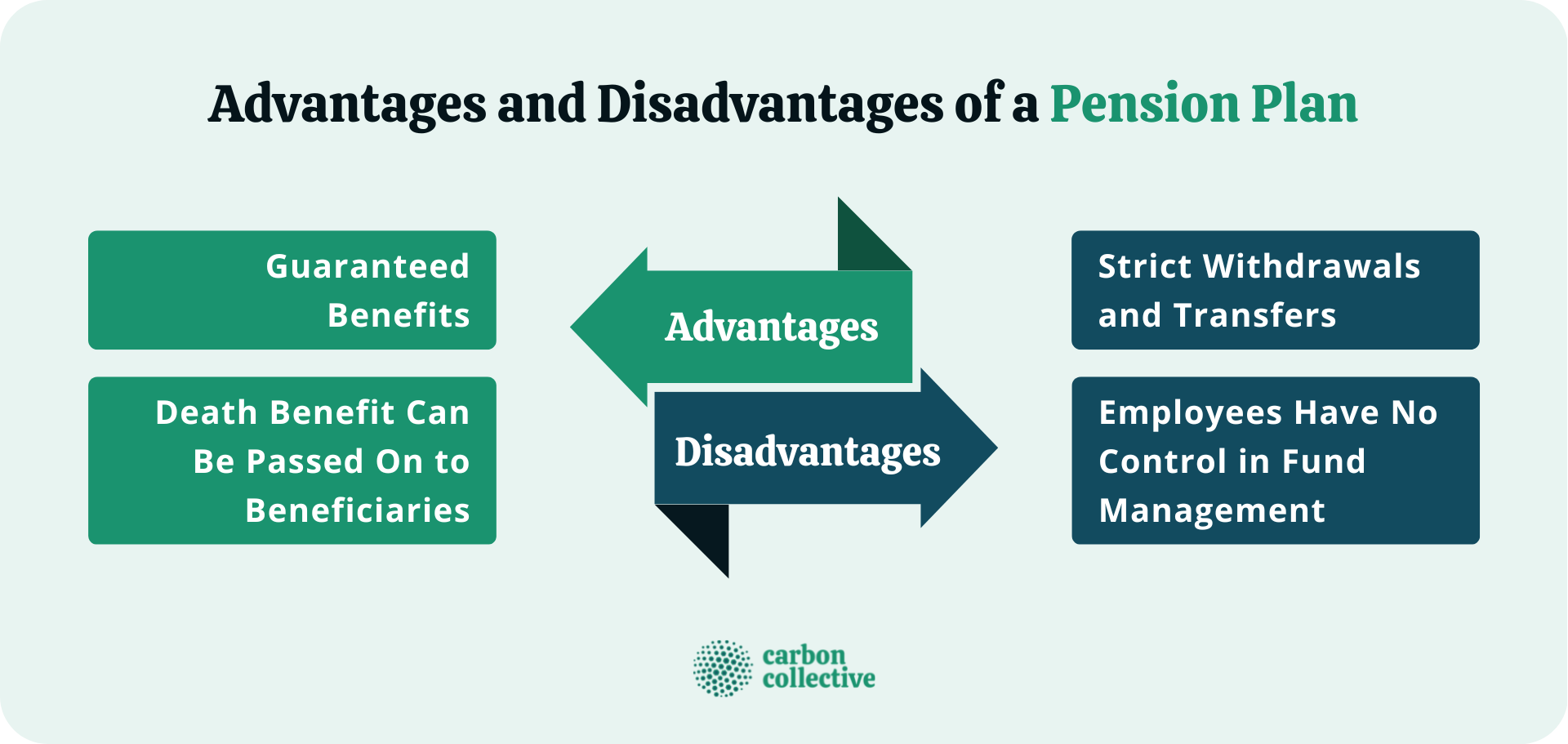
Guaranteed Benefits
One of the biggest advantages of a pension plan is that it provides guaranteed payments in retirement. This means that retirees can count on receiving a certain income each month, which can help cover living expenses and provide financial security.
Death Benefit Can Be Passed On to Beneficiaries
Another advantage of a pension plan is that, in most cases, any remaining benefits after the retiree's death can be passed on to beneficiaries (such as a spouse). This can provide an extra layer of financial security for loved ones.
Disadvantages of a Pension Plan
Below are some disadvantages of a pension plan:
Strict Withdrawals and Transfers
One downside of pension plans is that they typically have strict withdrawal and transfer rules. For example, in most cases, employees cannot access their pension benefits until they reach retirement age. Also, if they leave their job before retirement, they may be unable to take their pension with them.
Employees Have No Control in Fund Management
Another disadvantage of a pension plan is that employees generally have no say in managing their pension fund. The investment decisions are made by the employer or the pension fund manager, and employees cannot change the investments or allocations.
What Is a 401(k) Plan?
A 401(k) plan is also a retirement savings plan sponsored by an employer. It is a type of defined-contribution plan, which means that employees contribute a portion of their paycheck to the plan, and the employer may also make contributions.
The money in the 401(k) plan is then invested, and the account balance grows over time. Employees can withdraw the money from their account when they retire, typically as a lump sum or in installments.
Advantages of a 401(k) Plan
Below are some advantages of a 401(k) plan:
Tax-Deferred Contributions
One of the biggest advantages of a 401(k) plan (traditional) is that employee contributions are made on a pre-tax basis. This means that the money goes into the account before taxes are deducted, and it will not be taxed until it is withdrawn in retirement.
This can result in significant tax savings, as the money has the potential to grow over time without being subject to annual taxation.
Employee Has Control in Fund Management
Another advantage of a 401(k) plan is that employees can control how their account is invested. They can choose from various investment options, including stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. There are even sustainable 401(k) portfolios than give employees the option to not invest in fossil fuels. They can also change their investments at any time if they want to.
Employer Match
Some employers will also match a portion of employee contributions to a 401(k) plan. This can be an important source of extra income in retirement.
Portability
Another advantage of a 401(k) plan is that it is portable, which means that employees can take their accounts with them if they leave their job. In most cases, the money can be rolled over into a new employer's 401(k) plan or into an Individual Retirement Account (IRA).
Disadvantages of a 401(k) Plan
Below are some disadvantages of a 401(k) plan:
Investment and Management Risks
One downside of a 401(k) plan is that it involves investment and management risks. This means that the account's value can go up or down depending on how the investments perform.
Also, if employees do not manage their accounts carefully, they may have less money than they contributed.
No Guaranteed Payout Amounts
Another disadvantage of a 401(k) plan is that there are no guaranteed payout amounts. This means that employees could end up with less money in retirement than expected, based on the performance of their investments.
_Plan.png?width=1920&height=942&name=Advantages_and_Disadvantages_of_a_401(k)_Plan.png)
Similarities and Differences Between a Pension Plan and 401(k) Plan
There are some similarities between pension plans and 401(k) plans. For example, both types of plans are sponsored by employers and can provide a source of income in retirement.
A significant difference between the two is that pension plans are defined-benefit plans while 401(k) plans are defined-contribution plans. Another difference is that employees generally have more control over their 401(k) plan than their pension plan.
With a 401(k) plan, employees can choose their own investments and manage their accounts. With a pension plan, the employer or pension fund manager typically makes investment decisions.
Additionally, pension plans often have stricter withdrawal and transfer rules than 401(k) plans. For example, in most cases, employees cannot access their pension benefits until they reach retirement age.
With a 401(k) plan, employees can usually withdraw the money sooner if they need to.
Pension Plan vs 401(k) Plan: Which Is Better?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question. The best retirement savings plan for an individual will depend on factors such as age, income, retirement goals, and investment preferences.
However, it might be helpful to keep the following factors in mind:
- Pension plans do not require employees to make any contribution to the account. The employers are responsible for making all the contributions. At retirement, payouts are guaranteed.
- Employees are responsible for making contributions to their 401(k) accounts. An incentive for this is when the employer chooses to match the employee's contributions, as this is free money.
- 401(k) plans give account owners greater flexibility in investments and withdrawals than pension plans.
Final Thoughts
Pension plans and 401(k) plans are both employer-sponsored retirement savings plans. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, so there is no one-size-fits-all answer as to which is better.
The best retirement savings plan for an individual will depend on their personal circumstances.
When deciding which plan is right for them, employees should consider factors such as age, income, retirement goals, and investment preferences. Employees should also be aware of the risks involved with each type of plan.
Pension plans may have stricter withdrawal and transfer rules than 401(k)s, but they can also provide a guaranteed income stream in retirement.
401(k)s may require employees to contribute to the account, but they also offer more flexibility regarding investments and withdrawals.
Ultimately, the best retirement savings plan is the one that meets an individual's needs and goals.
FAQs
1. Do 401(k) plans allow borrowing of funds from the account?
Yes, 401(k) plans typically allow account holders to borrow from their accounts. However, there may be some restrictions on how the money can be used.
2. What happens to a person's 401(k) account when they leave their job?
When employees leave their job, they usually have the option to either cash out their 401(k) account or roll it over into another retirement savings plan, such as an IRA.
3. Can pension payments be taken as a lump sum?
Account owners of pensions have the option to either withdraw funds in a lump sum or in the form of an annuity, which is a series of payments over time.
4. What is the difference between a pension and an annuity?
Pensions are employer-sponsored retirement savings plans. Annuities are insurance contracts that can be used to generate a stream of income in retirement.
5. Can employees have both a pension plan and a 401(k) plan?
Yes, some employers offer both types of plans to their employees. However, employees are not required to participate in both plans.


